“We sent the campaign… but nobody opened it.”
You’ve probably heard that one before. Since Google and Yahoo tightened their email authentication rules in 2024, this story’s become all too common. Domains without proper DMARC setup started seeing open rates nosedive and reputations tank almost overnight.
For anyone running cold email campaigns, DMARC has gone from an optional add-on to becoming a vital passport into inboxes. Yet most treat it like a one-time setup task instead of the deliverability safeguard it truly is.
In this guide, we’ll break down what DMARC does, why it’s critical for cold outreach, and how pairing it with Instantly’s deliverability tools keeps your emails trusted, authenticated, and landing front and center in your prospects’ inboxes.
Understanding DMARC
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance.
It's an email authentication protocol that works alongside SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to verify that emails sent from your domain are legitimate (i.e., not spoofed, phished, or hijacked).
Sounds technical? That’s because it is. But the takeaway is simple:
- No DMARC policy means no domain credibility.
- No monitoring means no clue what’s not working.
When properly configured, DMARC tells email providers (like Gmail, Outlook, etc.) that you’re playing by the rules and that they can trust your emails. That trust translates to higher deliverability, fewer spam-folder occurrences, and more converted prospects.
Why DMARC Monitoring Matters
Let’s say you’re running cold outreach. You’ve warmed your domain, personalized your email campaign, and targeted the ideal customer profile. But somewhere in the system, one of your DNS records breaks.
You don’t notice, but Gmail does. Now your domain gets flagged, and prospects start marking your emails as spam.
A strict DMARC policy without monitoring is dangerous. Yes, it protects your brand from spoofing. But if something goes wrong, such as your email tool changing IPs, even legitimate emails may get rejected. And you won’t know unless you practice DMARC monitoring.
Think of it like installing a high-tech alarm system in your house, then turning your phone off. If it triggers, great, you’re protected. But if nobody’s watching the alerts, what’s the point?
What Does DMARC Monitoring Actually Do?
DMARC monitoring works like a real-time dashboard to protect your domain’s reputation. Once you publish a DMARC record with a RUA tag (that’s where reports get sent), you’ll start receiving forensic data about every email claiming to be from your domain.
A good monitoring tool uses those XML reports to help you answer questions like:
- Is someone spoofing my domain?
- Did my SPF record hit the lookup limit?
- Are all my sending tools properly authenticated?
- Which providers are rejecting or accepting my emails?
How Does DMARC Monitoring Affect Cold Email ROI?
Your cold email campaign lives or dies by deliverability. A small dip in inbox placement (even just 5%) adds up to dozens of missed opportunities over time.
You might end up scaling a broken system, dumping money into lead generation while actual conversions stall. Here’s how DMARC monitoring boosts ROI:
Fewer Lost Emails
Authentication failures can silently kill your cold emails without bounce notifications. DMARC monitoring gives you immediate visibility into alignment issues, helping you quickly pinpoint which services are failing.
Catching these problems early ensures your emails land in inboxes, not spam.
Improved Security
DMARC monitoring alerts you to unauthorized use of your domain, allowing you to take swift action against potential fraud that could harm both your reputation and your customers.
Better sender reputation
Providers like Google and Yahoo factor authentication into sender reputation. Monitoring ensures your emails consistently pass DMARC checks, proving your legitimacy and boosting open rates.
Faster Troubleshooting
Without monitoring, issues can go undetected for weeks. DMARC reports provide real-time insights, so you can spot and fix authentication problems before they affect your results.
What to Look For in a DMARC Monitoring Tool
Not all monitoring solutions are created equal. If you’re running outreach at scale, here’s what you must prioritize:
Aggregate Report Analytics
DMARC generates aggregate (RUA) reports that provide an overview of authentication results. You need charts, graphs, summaries, and alerts you can act on. A good DMARC monitoring tool translates these reports into actionable insights about:
- Policy application results.
- Authentication pass/fail rates.
- Volume patterns that might indicate abuse.
- Which IPs send email on your behalf.
Forensic Reports Review
If you’re experiencing deliverability issues, ensure that your DMARC monitoring tool provides forensic (RUF) reports.
These reports can pinpoint exactly why certain emails are failing, whether it's an SPF configuration issue, a DKIM key problem, or an alignment failure.
Real-Time Alerts and Notifications
The most valuable aspect of DMARC monitoring for high-volume senders is real-time alerts. When you're sending lots of cold emails through Instantly, you need a good monitoring tool that immediately notifies you when:
- SPF records need updating.
- DKIM keys are about to expire.
- Authentication failure rates spike.
- New unauthorized senders use your domain.
Subdomain Tracking
Many Instantly users employ dedicated subdomains for cold email campaigns to protect their primary domain's reputation.
A good DMARC monitoring tool tracks authentication across all subdomains, ensuring consistent policies throughout your email infrastructure.
Maximizing DMARC Monitoring for Cold Email Campaigns
DMARC monitoring is more than tracking reports. It’s about spotting issues early and making informed adjustments to keep your cold email campaigns on track. Here’s what to focus on:
Implement DMARC Policies Progressively
For Instantly users, it’s smart to phase in your DMARC policy instead of jumping straight to p=reject:
- Start with p=none: Monitors email traffic without affecting delivery, ideal for collecting data and identifying authentication issues.
- Move to p=quarantine: Suspicious messages are routed to spam, giving you more protection without full enforcement.
- Finally, switch to p=reject: Blocks unauthenticated emails outright, offering the highest level of domain protection.
This progressive approach helps you monitor the impact of DMARC on deliverability at each stage.
Monitor Alignment Regularly
Cold email deliverability relies on consistent authentication. That means your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records must align with the domain used in your "From" address.
Any misalignment, even from changing sending IPs, can affect inbox placement. Regular monitoring helps you catch these issues early, especially as your campaigns scale up.
Gain Competitive Intelligence
DMARC monitoring doesn’t just protect you—it gives you unexpected visibility into your email ecosystem. By analyzing who’s sending emails from your domain, you can uncover:
- Potential misuse or spoofing attempts by competitors.
- The third-party platforms your partners or vendors are using.
- Opportunities for integration or collaboration with legitimate senders.
Instantly and DMARC: A Power Combo
At Instantly, deliverability isn’t just a feature; it’s the backbone of what we do. That’s why we recommend DMARC monitoring to every serious sender.
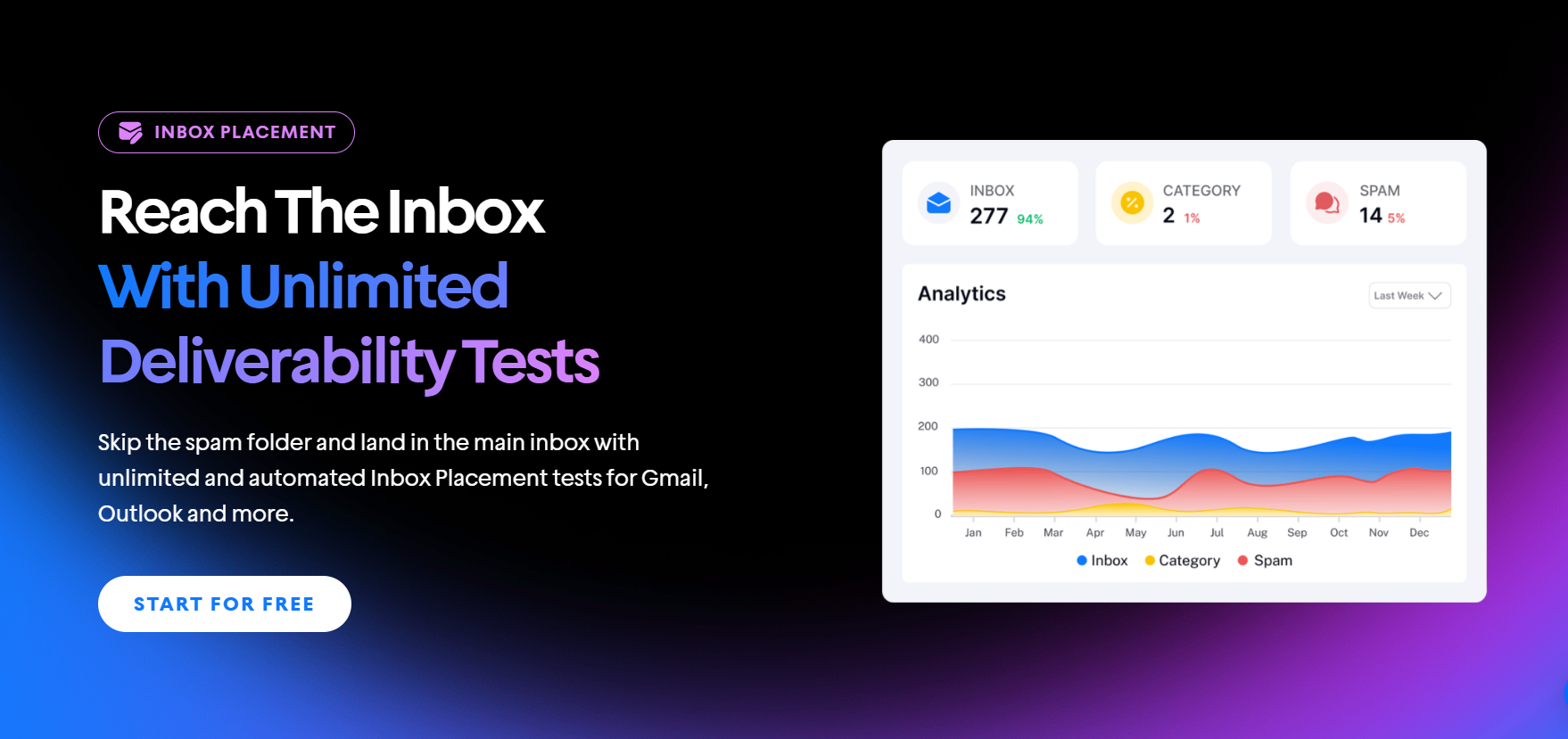
Don’t wait for your campaigns to tank before realizing something broke. Don’t leave your domain exposed to spoofers. And don’t assume that just because emails are sent, they’re getting delivered.
Instantly’s Done-For-You (DFY) email setup service gets your domain configured correctly from day one, so you can send with confidence. Start your free Instantly trial today and see why thousands of cold emailers trust us to deliver, every time.




