To master how to create an AI agent, you must architect a system that combines a core LLM "brain" with specialized tools, long-term memory, and iterative planning loops.
The process hinges on first rigorously defining the agent's core objective and operational scope, then architecting its reasoning process through frameworks like ReAct (Reasoning + Acting).
You'll also need to equip it with critical tools (API access, code execution, web search, etc.) and ground it in relevant, structured data. Finally, you'll need to rapidly prototype using no-code platforms or frameworks like LangChain, then test the agent's decision-making in simulated environments before a controlled, monitored deployment.
Picture your inbox right now. How many leads are waiting for a response? How many of those replies could you answer without even thinking: "yes, tell me more," "what's the pricing," "can we schedule a call?"
Now imagine something handling all of that for you. Not just sending canned responses, but actually reading each reply, understanding what the lead wants, and taking the right action. That's what AI agents do.
Most people misunderstand what an AI agent actually is. They confuse basic automation with true agentic behavior, or they expect magic solutions that don't exist yet.
By definition, an AI agent is software that makes decisions and takes action on its own to reach a specific goal. For cold email, that means an agent can read incoming replies, understand context, decide whether a lead is interested, send appropriate follow-ups, share calendar links, and update your CRM without you watching over it.
This guide walks you through exactly how to build an AI agent for cold email, from defining your goal to deploying a working system. You'll learn the core components every agent needs, the tools that make it work, and how to set it up without writing code.
What Is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is different from regular AI tools like ChatGPT. Regular AI waits for you to give it instructions and then responds. An AI agent takes initiative. It decides what needs to happen next and does it.
Think about your current cold email process. You write a sequence, send it out, then wait for replies. When they come in, you read each one, figure out if the lead is qualified, write a response, maybe book a meeting, then log everything in your CRM. That's five separate steps you handle manually for every single reply.
An AI agent takes over that process. It reads the reply, identifies intent (interested, has questions, wrong person, out of office), sends the right response, books meetings when appropriate, and updates your records. You set the goal once, and it executes.
The difference comes down to autonomy. AI agents use large language models (LLMs) as their decision-making engine, but they also connect to tools like email platforms, CRMs, and calendars so they can take action in the real world, not just suggest what you should do.
How to Build an AI Agent: 5 Steps
Building an AI agent for cold email doesn't require programming skills or AI expertise. You need the right components, the right tools, and clear instructions for what you want it to do.
Step 1: What do you want your AI agent to do?
Start by getting specific about the task. "Automate cold email" is too broad. You need to define exactly what success looks like and which actions the agent should take.
Ideally, write down each step your agent will handle. For example:
- Send personalized cold email sequences to 500 new prospects weekly
- Read and categorize all replies within 5 minutes
- Respond to questions with relevant information about your product
- Share calendar links when leads express interest
- Update lead status in your CRM automatically
You also need to decide how much oversight you want. Some teams prefer human-in-the-loop mode, where the agent drafts responses but waits for your approval before sending. Others use autopilot mode, where the agent sends automatically for common scenarios.
If you're starting out, go with human-in-the-loop first. You can switch to autopilot once you've confirmed the agent responds appropriately.
Step 2: Which tools and platforms work best?
You need three categories of tools to build a functional AI agent for cold email:
A "brain" (large language model). This powers the agent's ability to understand context and decide what to do next. Common options include:
- GPT-4 (OpenAI)
- Claude (Anthropic)
- Gemini (Google)
You don't need to build your own model. Most platforms let you plug into these LLMs through APIs.
Tools the agent can use. Your agent needs access to actual systems so it can take action, not just suggest what to do. Essential tools for cold email include:
- Email sending platform (for sequences and replies)
- Lead database (to find and verify contacts)
- Calendar system (to book meetings)
- CRM (to update lead status and log activities)
An orchestration layer. This connects the brain to the tools and tells the agent which tool to use when. Options include:
- Zapier
- Make (formerly Integromat)
- n8n
Each platform has different complexity levels. Visual builders like Make are easier for non-technical users, while n8n offers more customization if you need it.
Step 3: How do you set up the core components?
Every AI agent needs four foundational pieces to function:
Brain (the reasoning engine): The LLM processes incoming information and figures out what to do next. When a lead replies, "Tell me more about pricing," the brain understands intent and determines the appropriate response. You configure the brain by giving it clear instructions about your product, target audience, and how to handle different scenarios. The more specific your instructions, the better it performs.
Memory (context retention): The agent needs to remember past interactions. If someone asked about your pricing last week and now wants to schedule a demo, the agent should reference that earlier conversation. Memory prevents the agent from repeating itself or losing track of where each conversation stands.

Most platforms store conversation history automatically, but you need to define what information matters most and how long to retain it.
Tools (taking action). Connect each tool from Step 2 to your agent by setting up API keys, granting permissions, and testing that data flows correctly—your agent needs access to create calendar events, send meeting invites, and update contact records in your CRM. Be sure to test every connection before going live, as one broken link can stop your entire workflow.
Instructions (boundaries and rules). Define what the agent can and cannot do. You might set rules like "never discount more than 15%" or "always escalate enterprise deals to human sales reps." Clear instructions prevent the agent from making choices outside your comfort zone.
You also need fallback options for edge cases. What should the agent do if someone asks an unusual question? How should it respond to angry replies? Build in backup plans so the agent doesn't freeze when it encounters something unexpected.
Step 4: How do you add control and oversight?
You wouldn't hand someone the keys to your business email and say, "Figure it out." Start by assuming the agent will misunderstand something. It will. The question isn't if, but when. So you need systems in place to catch mistakes before they reach your prospects.
Begin with human-in-the-loop mode. The agent drafts responses and sends them to you for approval before anything goes out. This could be through Slack, email, or your platform's dashboard. Review what it suggests, approve good responses, and reject bad ones. After a few dozen iterations, you'll spot patterns and know where to tighten your instructions.
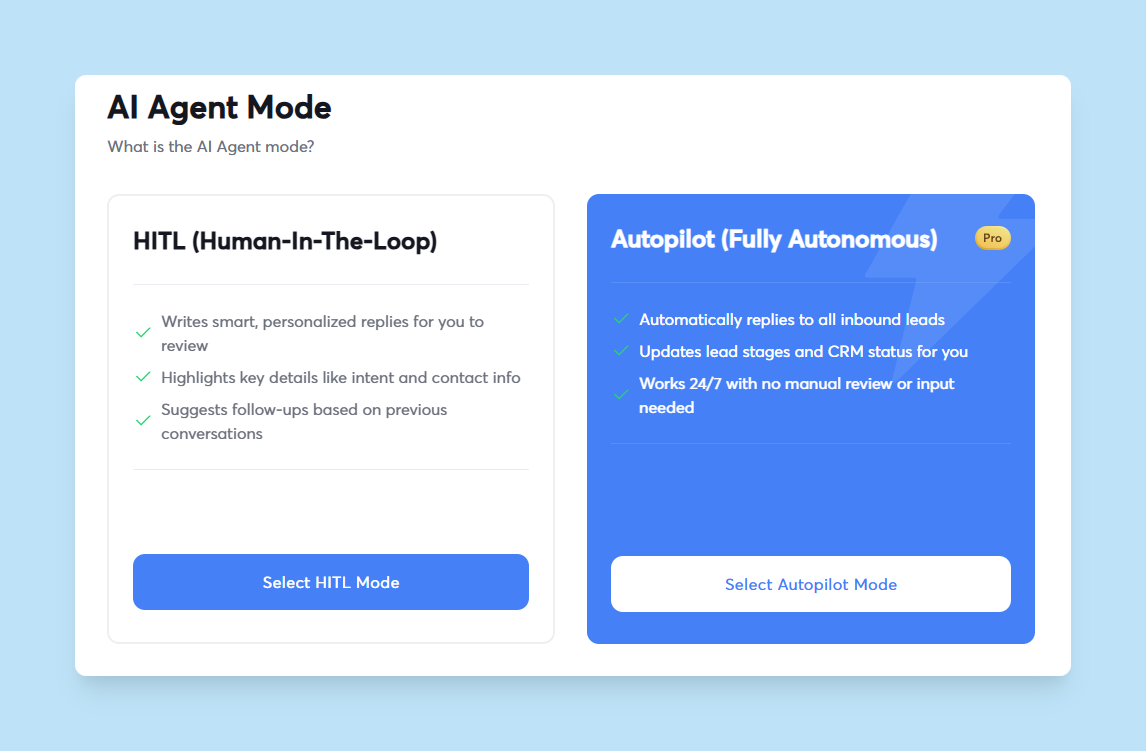
Set approval thresholds. The agent can handle simple questions automatically, but needs your sign-off for anything complicated. For example, auto-respond to "What industries do you work with?" but require approval for pricing negotiations or custom contracts. Define these rules explicitly so the agent knows when to act and when to wait.
Monitor what matters. Track response times, reply rates, meeting bookings, and conversion rates. If the agent's replies get lower engagement than your manual messages, investigate why. You might need to adjust tone, timing, or how it handles specific objections.
Build feedback loops. Create a simple way to flag responses as good or bad. When you approve a response, note why it worked. When you reject one, explain what was wrong. Use this data to refine your instructions and improve accuracy over time.
As your volume grows, you'll want to adjust oversight levels. High-volume, low-stakes interactions can run on autopilot, but high-value enterprise deals still need human review. The goal is to find the right balance between speed and control for each scenario.
Step 5: How do you test and launch?
Don't skip testing. One bad response to a hot lead can cost you a deal, and you won't know your agent messes up until it's too late.
Start with a small test group. Pick 50-100 leads from your list and let the agent handle their outreach. Don't scale yet. Monitor every interaction closely. You'll quickly spot gaps in your instructions or problems with tool connections that you missed during setup.
Test different scenarios. Send test emails that trigger various responses: interested leads, objections, out-of-office replies, wrong contact, and requests for more information. Make sure the agent handles each scenario appropriately. If it doesn't, adjust your instructions and test again.
Check deliverability health. If you're using the agent to send cold emails, warm up your domains properly first. Poor sender reputation will tank your results regardless of how smart your agent is. Send gradually increasing volumes over 2-3 weeks while monitoring bounce rates and spam complaints. Most platforms track this automatically, but you need to actually look at the data.
Validate data accuracy. Confirm that lead information, meeting bookings, and CRM updates are logging correctly. Click through a few booked meetings to verify that calendar invites went out. Check your CRM to see if lead statuses updated properly.
Once testing proves the agent works reliably, scale gradually. Double your volume each week while watching the metrics. If performance stays consistent, keep going. If you see drops in reply rates or increases in spam complaints, pause and figure out what changed before continuing.
Your agent will improve as it runs. You'll spot new edge cases, refine instructions, and adjust thresholds based on real data. The goal is to reach a point where you check in weekly instead of daily, then monthly instead of weekly.
Build Your Cold Email AI Agent with Instantly
As you can see, building an AI agent from scratch means connecting multiple tools, writing instructions, testing integrations, and troubleshooting when things break.
Or you can use a platform designed specifically for cold email that handles the setup for you. Instantly combines the three core components you need (email infrastructure, AI intelligence, and CRM functionality) into one system built for outreach workflows.
Instantly Copilot acts as your AI agent for building and managing cold email campaigns. You describe what you need in plain language, and Copilot generates complete email sequences, suggests qualified leads based on your ideal customer profile, and creates full campaigns in minutes.
The AI Reply Agent handles incoming responses autonomously. It reads every reply, categorizes intent, and takes appropriate action. In autopilot mode, it sends responses within 5 minutes. In human-in-the-loop mode, it drafts replies and routes them to your team for approval via Slack before sending.
When a lead shows buying intent, the agent automatically shares your calendar link to book meetings. It also handles common objections by referencing your knowledge base and product details, and keeps your CRM updated by logging all interactions and lead status changes.
Unibox consolidates all replies from every connected email account into one interface. You can manage hundreds of conversations without losing context, and the AI categorizes each message automatically using custom labels you define.
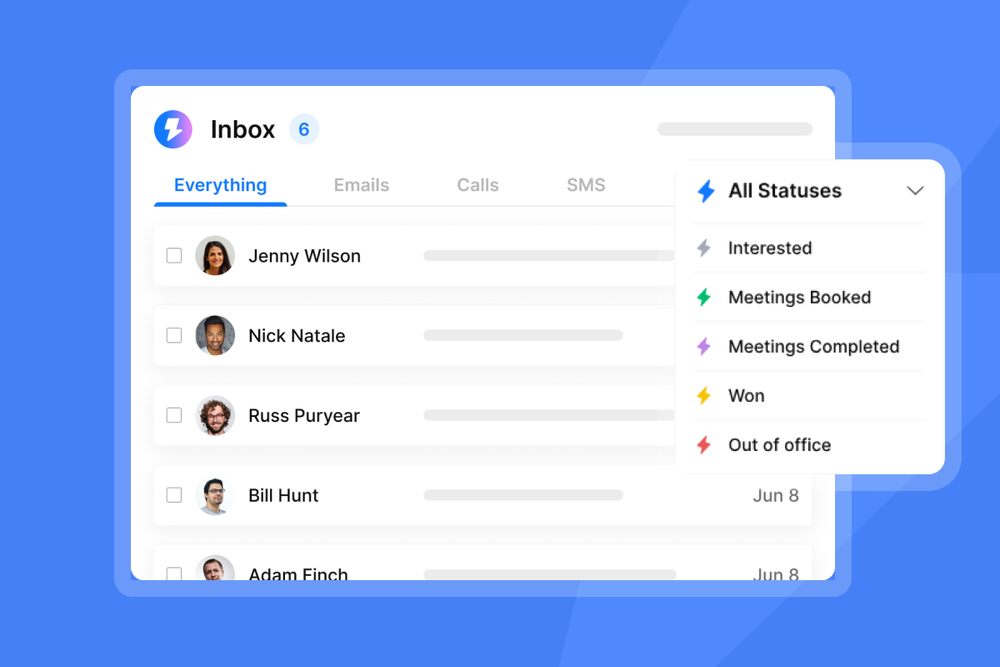
Unlimited email accounts and warmup are included in all plans, so you can scale sending volume without per-seat fees. The platform monitors deliverability health automatically and pauses campaigns if it detects issues, protecting your sender reputation.
Campaign performance tracking shows opens, replies, meetings booked, and pipeline value. You can see exactly which messages and sequences drive results, then let Copilot generate variations to test.
Instantly's credit-based pricing means you pay for what you use rather than per user or per seat. This makes it economical for agencies managing multiple client accounts or sales teams running high-volume outreach.
Key Takeaways
AI agents handle the work that keeps you stuck in your inbox: reading replies, qualifying leads, and sending follow-ups. But they only work if you set them up right.
You need four components: a brain (LLM), tools (email platform, CRM, calendar), memory, and clear instructions. You can connect these yourself using platforms like Zapier or n8n. Or you can use a system like Instantly that comes pre-built for cold email.
Want to skip the setup? Start your free trial with Instantly and see how AI agents turn cold email into booked meetings and closed deals.




